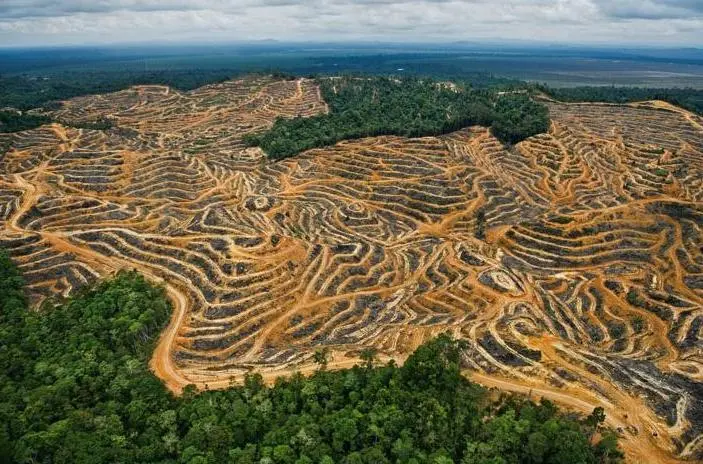

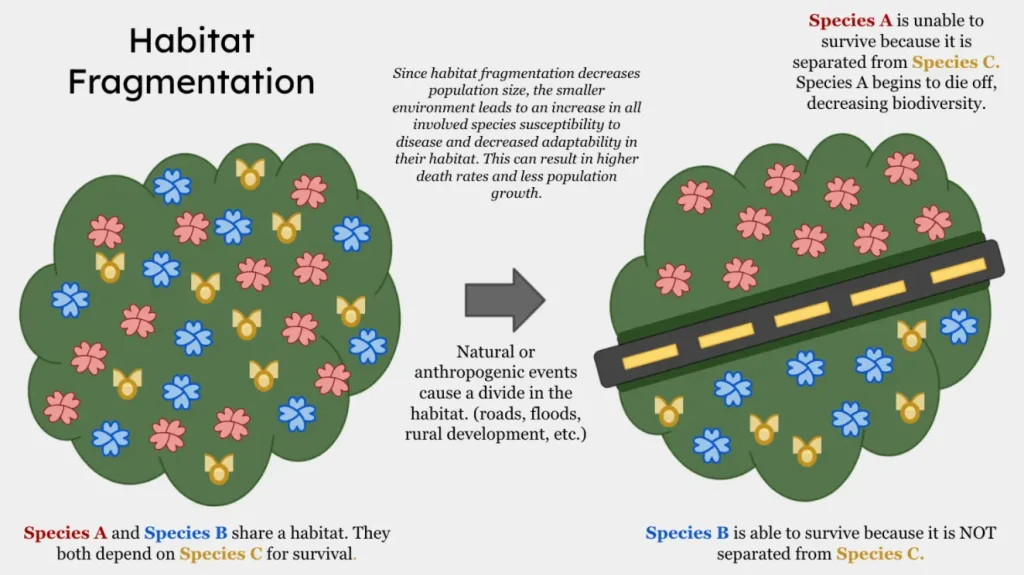
One of the main issues affecting ecosystems globally is habitat fragmentation, which is the division of large and interconnected habitats into smaller, separate regions. Human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, infrastructural development, and agricultural growth are the main drivers of habitat fragmentation.
Habitat Fragmentation
When areas of habitat are wiped out, smaller and disconnected regions remain behind, causing habitat fragmentation. While natural events like volcanic eruptions or fires might cause this, human action is usually to culpability.
Habitat fragmentation occurs when the topography is changed in an approach that stumps the animals and interferes with their ability to live a normal life. When highways are built in the middle of forests and other natural regions, it causes habitat loss.
Even while habitats are not destroyed, habitat fragmentation however threatens the environment. Animals may become inaccessible from each other and food supply due to fragmentation, which might hamper their ability to survive.
This type of habitat loss arises on land as well as in water. Underneath the water, artificial topographies such as dams regularly act as barriers between species, making it more thought-provoking for them to find food and partners. Disparaging ecosystems contradicts the benefit of migration for the crowd of creatures whose survival depends on it.
A further importance of fragmentation is the edge effect. Several species, such as some lichens and mosses, favor moist, shaded environments. A dwindling section of forest may expose them to extreme sunlight or dry winds, causing them to disappear.
The most comprehensive home range of an organism will be maintained by a forest that is in good health. Fragmentation can seriously harm typically the top predators. The ecology can be severely disturbed if they disappear since they regularly have a vital role in controlling the numbers of other organisms.
Causes of Habitat Fragmentation
Several artificial factors and naturally occurring factors can cause habitat fragmentation, which divides and reduces continuous environments. Urbanization, roads, and agricultural practices are the main things that divide natural regions. Wildlife is commonly severely affected by this.
Given that habitat loss causes adverse environmental effects and wildlife deaths, one would sensibly wonder why we continue these practices that threaten biodiversity.
Agricultural Activity
Compared to earlier times, when farms were small-scale processes managed by local communities and families, nowadays, farming is a large industry that multinational companies can handle.
Nowadays, the agriculture sector produces food in large quantities that can be quickly and cost-effectively marketed. More land needs to be cleared to make more food, which requires more area to be cleared.
Business
Major corporations and businesses are destroying a lot of the environment. To expand and grow, these companies require more and more land. Many enterprises and firms have been sacrificed for business, standing where wild organisms and natural ecosystems once existed.
One well-known example is palm oil. Palm oil farms are grown throughout the tropics to meet the demand. Food items, laundry powders, cosmetics, and biofuels are all produced with palm oil.
Human Causes
Habitat Fragmentation is a common anthropogenic cause. When people clear out natural areas, it happens. This is done to create space for farming, the construction of infrastructure, and the construction of hydropower reservoirs.
As a result, a large, complete environment turns into a smaller one. Following the clearance of these places, we were left with little natural areas divided by farms, undeveloped territory, or open spaces.
Natural Causes
The fossil record comprises evidence of habitat destruction due to natural events such as volcanoes, fires, and climate change. For example, the breakdown of the European rainforest approximately 300 million years ago caused several issues for amphibians. However, as the temperature increased, additional variabilities of reptiles appeared during the same period.
Human Residence
Most natural ecosystems are regularly destroyed to make room for building homes for people. The land is cleared for important buildings and more money-making attractions. However, natural ecosystems are occasionally destroyed to create room for people to live there. To pay for their materials to create contented things for humans, they are also destroyed.
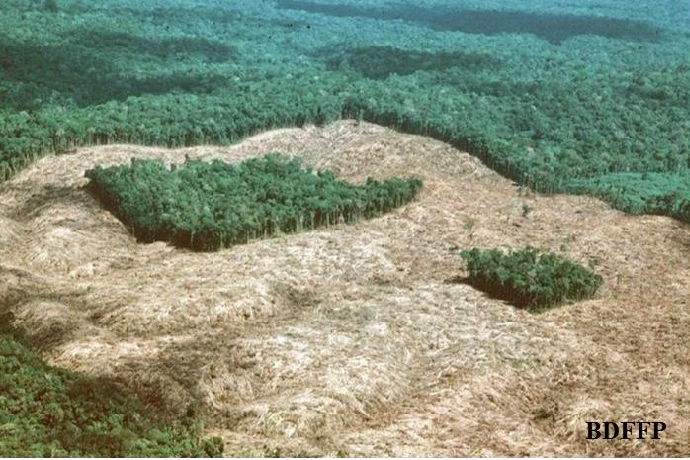

Effects of Habitat Fragmentation
The multiple effects of habitat fragmentation may significantly impact the pliability and effectiveness of ecosystems. To respond to the adverse effects on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning, conservation activities must be focused on habitat restoration, the creation of wildlife corridors, and the adoption of sustainable land-use practices.
So How is Habitat Fragmentation Related to Biodiversity Loss? An article by Earth.org https://earth.org/how-does-habitat-fragmentation-affect-biodiversity/
Increased Stress on Wildlife
A level surface must be definite while making land for residences and other structures to maintain steadiness throughout the building process. To achieve this, excavators regularly remove trees and level the ground in forest areas.
Unfortunately, animals don’t have time to adapt to such important changes in their surroundings because these changes happen so quickly.
Diminishes Soil Quality
When examining the effects of habitat loss, it is also needed to consider the ground. Due to the rapid changes in soil structure and quality that deprive plants nutrients and space they require to flourish; many plants can no longer thrive.
Additionally, many plants cannot adapt themselves to develop because of how tightly human technology has crowded the soil; if seeds are not disseminated elsewhere, the plant kind may become extinct completely.
Habitat Fragmentation Unbalance the Ecosystem
Nature uses ecosystems to keep a balance between several species and their surroundings. In the wild, everything is entangled, and life is automatic. Everything has its function, even the biggest trees and grass blades. Animals depend on one another and the earth for survival.
They regularly become mixed up and bewildered when the ecosystem gets upset by this equilibrium, putting them in danger. The outcome is death and the inability to produce and maintain the species.
Expose Wildlife to Unfriendly Conditions
Animals store food and water to survive hard times or when seasonal variations prevent them from accessing their usual food source. Natural shelters are similar to human residences in bad weather, providing protection from storms, intense heat, and torrential rain.
Their dislocation disturbs the entire way of life of wildlife. Many animals depend on their environments as safe havens from raptors. Additionally, young animals in the wild need a variation of care; they need to be trained in the skills necessary for collecting and hunting food, as well as protected from enemies during their most susceptible phases.
Loss of Natural Landscape
The land is smoothed to create homes, buildings, and other infrastructures. Land and trees are leveled with the help of bulldozers. Animals cannot alter these significant changes promptly due to the quickness of this process. Endangered ecosystems are the most common natural landscapes that are transformed for human purposes.
Solutions to Habitat Fragmentation
The reconnection, preservation, and management of fragmented ecosystems require a multimodal method to address habitat fragmentation. Nevertheless, the negative impacts of habitat fragmentation, there are several strategies we can implement to address this issue.
Develop Guidelines to Protect Natural Habitat
Regulation and guidelines are just as significant. Rules and plans should be established to let it for the legal alteration of a specific region for human benefit. As for biodiversity concerns, we may give species enough time for growth and more areas to remain unchanged by exercising greater control.
Understanding the Importance of Natural Resources
Protecting natural resources and considering how to utilize them in a way that doesn’t need the consistent destruction of habitats are two major ways we can fight habitat loss.
Create Awareness
In addition to education, raising awareness is a necessary step. Whenever the chance to securely record the method of habitat loss presents itself, observers must make it their mission to support reporting specialists.
The awful situations that environmental degradation can lead to are better demonstrated by images and videos, which cause strong feelings in viewers and inspire them to safeguard natural areas.
Habitat Restoration
Not only should efforts to preserve habitat emphasize minimizing the use of natural resources, but habitats that have been degraded also need to be restored. Rebuilding, managing continuously, and protecting the habitats are the steps that lead to habitat restoration.
Signs representing marine protected areas may irregularly be seen, but preservation organizations characteristically restore these areas. When visiting those regions, everyone should care more for the surrounding environment. This attempt aims to restore living and nonliving variables to their pre-human state.
Rebuild Habitats
Humans can harm natural ecosystems at a rate that should match their willingness to assimilate and try to replace what has been lost. If specific habitats are unsalvageable, we can help finance the formation of other regions that will act as a harbor for displaced wildlife.
These safe havens are similar to the natural environments where healthy living is likely for animals and plants without fear of destruction. Worldwide, Environmentalists have worked to establish these sanctuaries to avoid the extinction of several species.
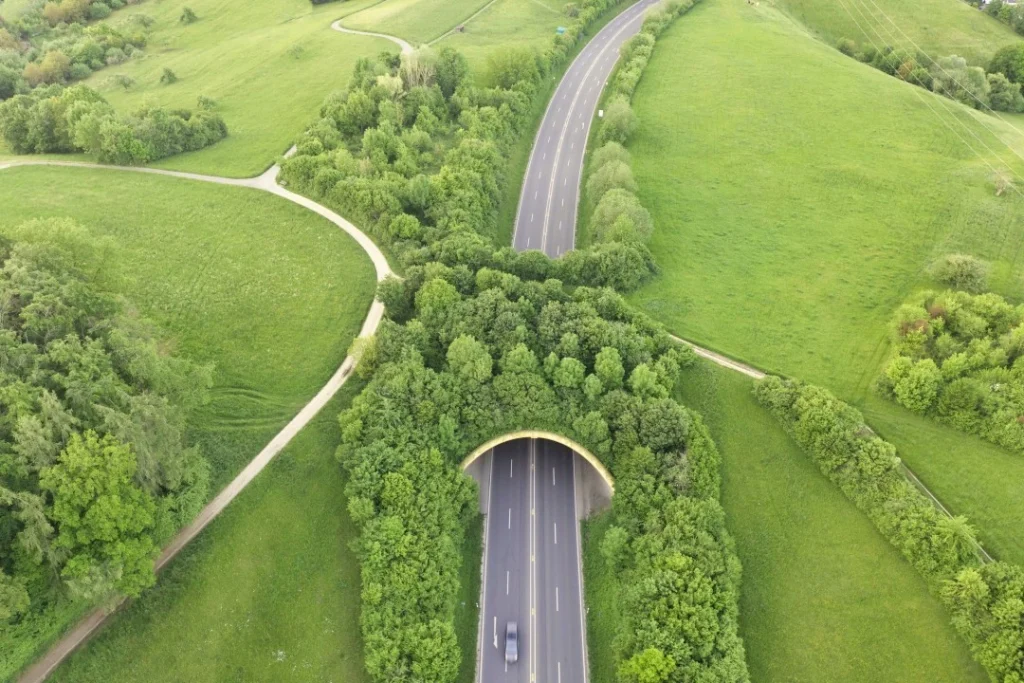

Conclusion
The problem of habitat fragmentation is severe and has negative consequences for ecosystems, biodiversity, and human welfare. Natural landscapes worldwide are still being disturbed by their causes, which are human activities, such as infrastructure development, agricultural growth, and urbanization.
We can assure a sustainable future for the environment and humans by recognizing the complicated dynamics of habitat fragmentation and accepting our communal duty to protect and restore habitats. We can also protect ecosystem resilience and biodiversity.
 The Climent Respect your roots, Protect your planet
The Climent Respect your roots, Protect your planet
